串的相关算法
Were equations, pictures or diagrams not properly rendered, please refresh the page. If the problem persists, you can contact me.
一、串的基本操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MaxSize 100
//定长顺序存储结构
// struct typedef{
// char str[MaxSize]; //MaxSize表示已经定义的变量,表示串的最大长度,因为多了个结束标记所以数组大小加一
// int length;
// }Str;
//动态分配存储表示(更加常用)
typedef struct Str{
char *ch;
int length;
}Str;
//串的基本操作
//1.赋值操作
int str_assign(Str* string, char *ch){
if(string->ch){
free(string->ch); //释放原串空间
}
int len=0;
char *c = ch;
while (*c) { //求ch串的长度
++len;
++c;
}
if(len == 0){ //如果赋值的是空串,直接返回空串
string->ch = NULL;
string->length = 0;
return 1;
}
else{
string->ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (len+1));
if(string->ch == NULL){
return 0;
}
else{
int i;
c = ch;
for(i=0;i<=len;++i,++c){
string->ch[i] = *c; //数组直接得就是指针(详细的就不说了),这样相等完全没问题
}
string->length = len;
return 1;
}
}
}
//2.取串长度操作
//略,直接结构体里面就有
//3.串比较操作
int str_compare(Str string1,Str string2){
int i;
for(i=0;i<string1.length && i<string2.length;i++){
if(string1.ch[i] != string2.ch[i]){
return string1.ch[i] - string2.ch[i];
}
}
return string1.length - string2.length;
}
//4.串连接操作
int concat(Str* string, Str string1, Str string2){
if(string->ch){
free(string->ch); //释放原串空间
string->ch = NULL;
}
string->ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (string1.length+string2.length + 1));
if(string->ch == NULL){
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
while (i<string1.length) {
string->ch[i] = string1.ch[i];
++i;
}
int j=0;
while (j<=string2.length) { //把结束标识也赋值进去
string->ch[i+j] = string2.ch[j];
++j;
}
string->length = string1.length + string2.length;
return 1;
}
//5.求子串操作(这他娘就是切片嘛)
int substring(Str* substr,Str string,int pos,int len){
substr->ch = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(len+1));
int i = pos;
int j = 0;
while(i<pos+len){ //结束时候的j大小为len。下一次就不能进行了,只能自己赋值结束符号
substr->ch[j] = string.ch[i];
++i;
++j;
}
substr->ch[j] = '\0';
substr->length = len;
return 1;
}
int main(){
Str string;
string.length = 0;
string.ch = NULL;
Str string1;
string1.length = 0;
string1.ch = NULL;
Str string2;
string2.length = 0;
string2.ch = NULL;
str_assign(&string1,"defsfasasf");
// printf("%d", string1.length);
// printf("%s", string1.ch);
str_assign(&string2,"abc");
// printf("%d", string2.length);
// printf("%s", string2.ch);
//printf("%d", str_compare(string1,string2));
// concat(&string,string1,string2);
substring(&string,string1,0,2);
printf("%d", string.length);
printf("%s", string.ch);
return 0;
}
二、模式匹配算法
-
基本模式匹配
int Index(SString S, SString T, int pos){ int i=pos, j=1; while(i<=S.length && j<=T.length){ if(S.ch[i] == T.ch[j]){ ++i; ++j; //继续向后比较 } else{ i = i - j + 2; //关键理解点,因为是i-(j-1)+1,i递增(移动)的时候j也在递增,所以不能i+1了事。i-(j-i)就是i开始 j = 1; //时候的位置,+1就是i前进一位 } } if(j>T.length){ return i - T.length; //返回找到的位置 } else{ return 0; } } -
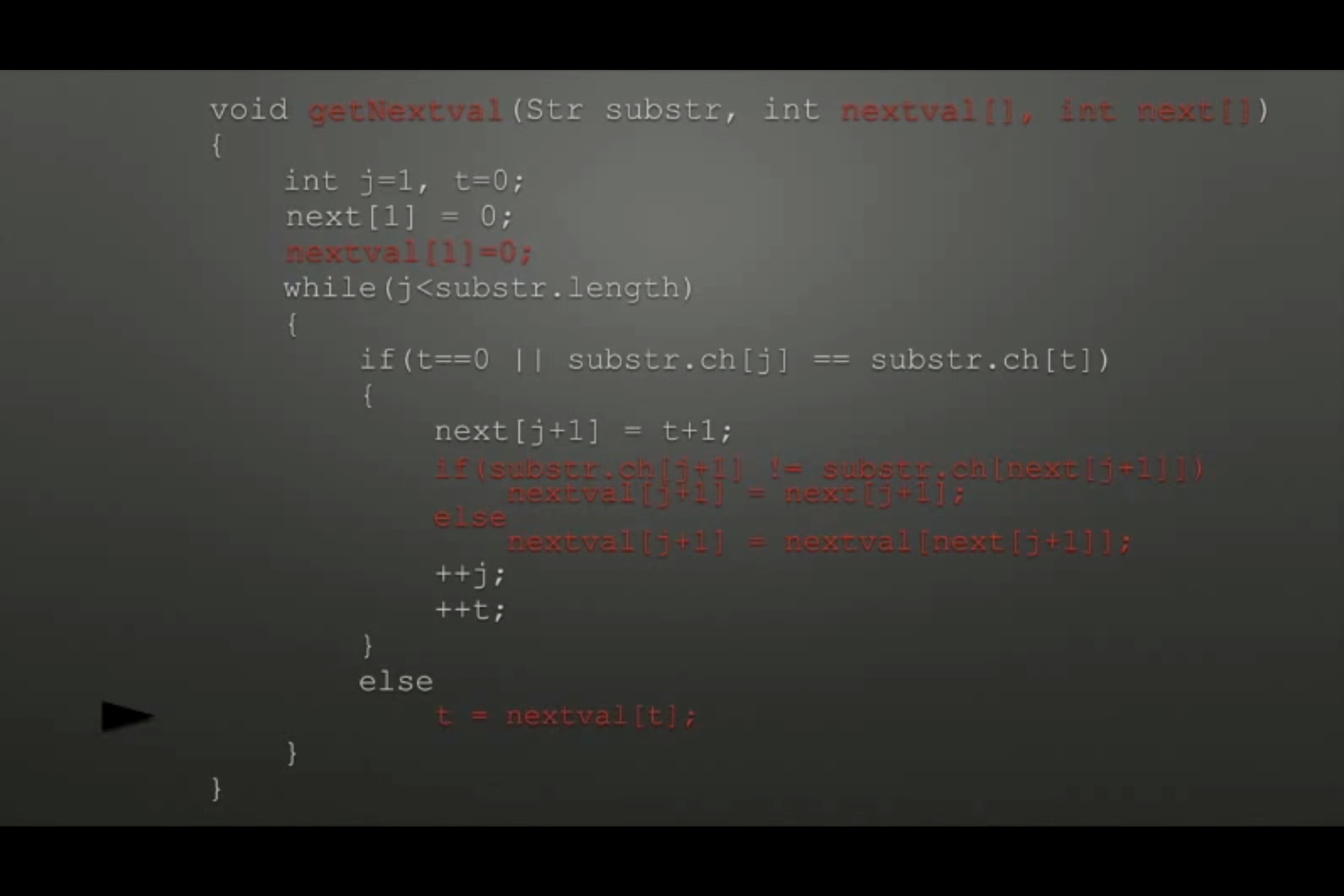
KMP算法(关键就在于如何求next[],我们已经知道next[j],现在求next[j+1])

void get_next(String T, int next[]){ int i = 1, j = 0; next[1] = 0; while(i<T.length){ if(j == 0;T.ch[i] == T.ch[j]){ ++i; ++j; next[i] = j; } else{ j = next[j]; } } } -
KMP算法的改进(对next数组的改进,升级为next_val数组)

Comments
😅 Commenting is disabled on this post.